模板1-最简单的通用框架模板
GPIO子系统#
在硬件上如何确定GPIO引脚?它属于哪组GPIO?它是这组GPIO的哪个引脚?需要2个参数。
但是在LInux软件上,可以使用引脚编号(所有的组所有的引脚都一起编号)来表示
知道引脚编号后,就可以使用GPIO子系统的函数了。下表列出了gpio子系统相关的函数,左边是新的函数,右边是旧的。
| descriptor-based | legacy |
|---|---|
| 获得GPIO | |
| gpiod_get | gpio_request |
| gpiod_get_index | |
| gpiod_get_array | gpio_request_array |
| devm_gpiod_get | |
| devm_gpiod_get_index | |
| devm_gpiod_get_array | |
| 设置方向 | |
| gpiod_direction_input | gpio_direction_input |
| gpiod_direction_output | gpio_direction_output |
| 读值、写值 | |
| gpiod_get_value | gpio_get_value |
| gpiod_set_value | gpio_set_value |
| 释放GPIO | |
| gpio_free | gpio_free |
| gpiod_put | gpio_free_array |
| gpiod_put_array | |
| devm_gpiod_put | |
| devm_gpiod_put_array |
在开发板上使用如下命令可以查看已经使用的GPIO:注意在软件上是从0开始编号的,而在6ull芯片手册里是从1开始编号的。
怎么确定GPIO引脚的编号?
- 先在开发板的/sys/class/gpio目录下,找到各个gpiochipXXX目录(XXX是这一组的其实编号)
- 然后进入某个gpiochipXXX目录,查看文件label的内容,就可以知道起始号码XXX对于哪组GPIO(物理地址上的组别)
那么GPIO4_14的号码是96+14=110,可以如下操作读取按键值:
注意:如果驱动程序已经使用了该引脚,那么将会export失败
对于输出引脚,假设引脚号为N,可以用下面的方法设置它的值为1:
中断函数#
使用中断的流程:
确定中断号
注册中断处理函数,使用的函数原型如下:
在中断处理函数里
- 分辨中断
- 处理中断
- 清除中断
函数细节:
request_irq函数第1个参数是中断号,可以根据GPIO函数获得中断号:
request_irq函数第2个参数是函数指针,指向中断处理函数:
request_irq函数的第3个参数表示中断触发条件,有如下取值:
request_irq函数的第4个参数是中断的名字,可以在执行cat /proc/interrupts的结果里查看。
request_irq函数的第5个参数是给中断处理函数使用的,中断处理函数的第二个参数就是这个参数。
模板解读#
04_template1_gpio_drv
file_operations
GPIO的操作
中断的处理
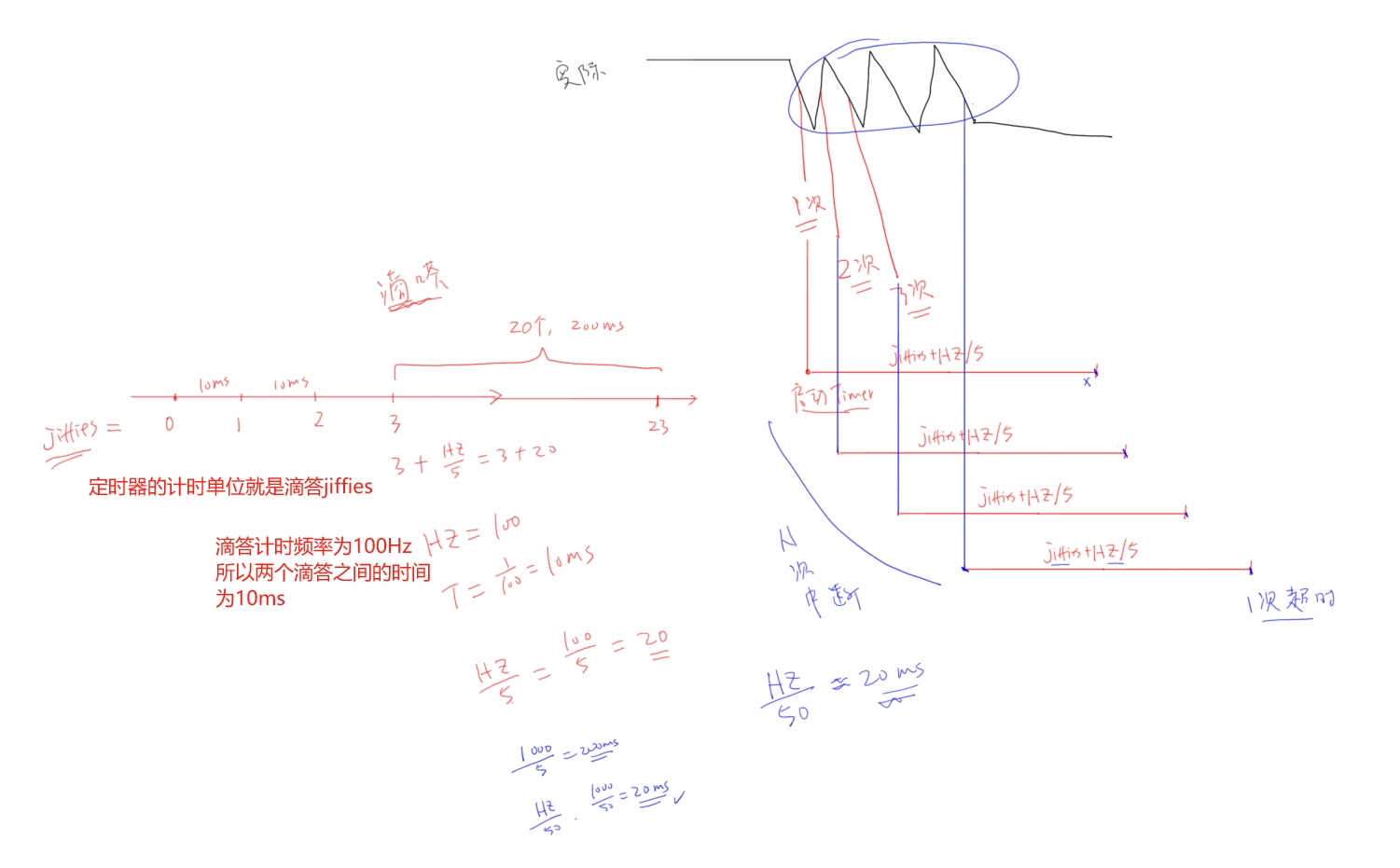
定时器
使用定时器进行按键消抖,在按键中断里延长定时器时间,这样多个按键中断,只会触发一次定时器超时;在定时器超时处理函数里进行按键值读取与保存。
交互流程解读#
非阻塞 具体阻塞与否,在于驱动程序有没有判断标记。
阻塞
wait_event_interruptible函数原型:等待condition事件为真,上述代码是等待“buf非空”事件 为真;如果condition不成立,就进入休眠并把它放入wq队列中,此时就需要其他函数调用wake_up()把它唤醒。
当按键按下时,经过定时器延时消抖后,调用定时器的中断函数:使用wake_up_interruptible唤醒gpio_wait队列中的值
POLL
- 有data,立即返回
- 无data,休眠
- 被唤醒,a.按下/松开 b.超时
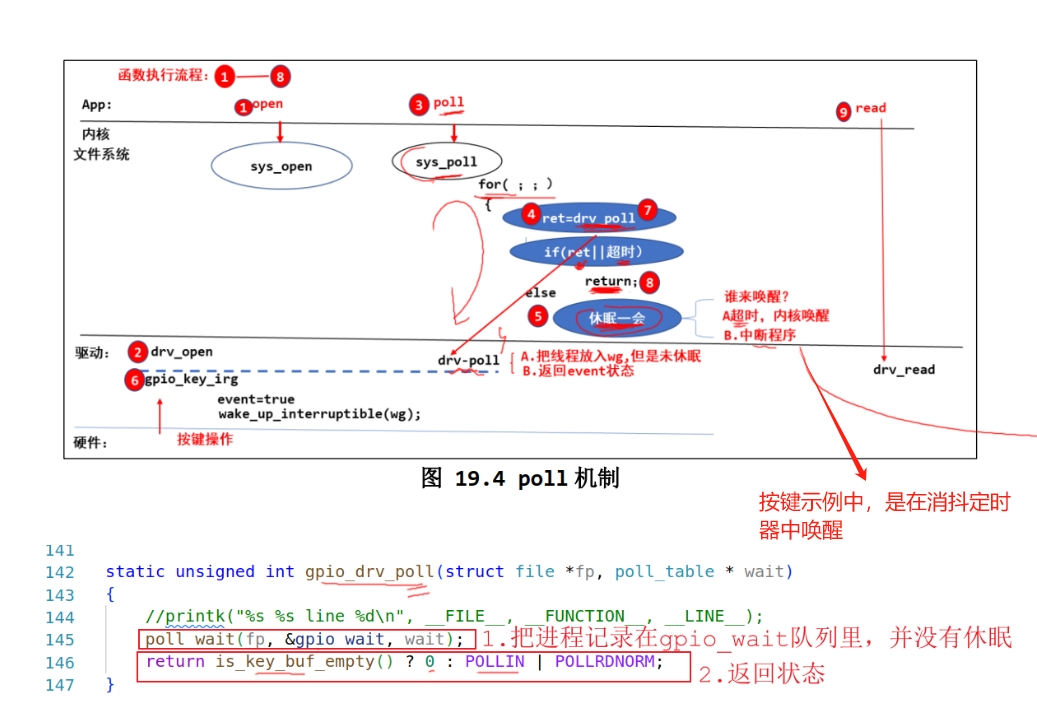
应用程序的poll调用sys_poll,然后sys_poll中有一个循环,会先调用驱动程序的drv_poll,如果驱动程序的返回值不为0或者超时,就返回,否则进入休眠。
drv_poll:把线程放入wq中,但是未休眠;返回当前event状态(有数据返回POLLIN | POLLRDNORM,无数据返回0)
内核sys_poll函数进入休眠,谁来唤醒?a.超时,内核唤醒;b.中断程序唤醒gpio_key_wait队列
异步通知 发信号:中断/定时器的函数发送信号(主),APP(宾) APP:
驱动:
进程的信息隐藏在button_fasync结构体里: 在APP中修改了flags,即调用fcntl(fd, F_SETFL, flags | FASYNC);时,会导致驱动程序的.fasync = gpio_drv_fasync函数被调用。所以在驱动定时器中断函数里就可以发信号给进程。
当app接收到信号后就会运行sig_func函数,执行完后就会回到main函数。
补充环形缓冲区#
适合A放入值,B取出值的场景,可以很好地管理值和防止值丢失。
请点击左侧菜单(移动端为右下角)选择要查看的所有笔记吧。